"Low Voltage Switchgear Explained: How It Keeps Power Systems Safe, Stable & Smart"
Day 89 of my 100-day journey into India's power sector.
From lighting up homes to powering industrial machines, low voltage (LV) switchgear plays a silent yet critical role in keeping modern electrical systems running safely.
In this post, we break down:
What LV switchgear is
The structure of an LV distribution board
Role of ACBs, MCCBs, ELCBs, and fuses
How different feeders are protected
What Is Low Voltage Switchgear?
Low Voltage Switchgear refers to electrical switchgear rated up to 1kV. It includes:
Circuit breakers
Switches
Isolators
HRC fuses
Miniature circuit breakers (MCBs)
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs)
Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers (ELCBs)
Their job? Protect LV systems from overloads, short circuits, leakages, and other faults— while allowing safe and efficient control.
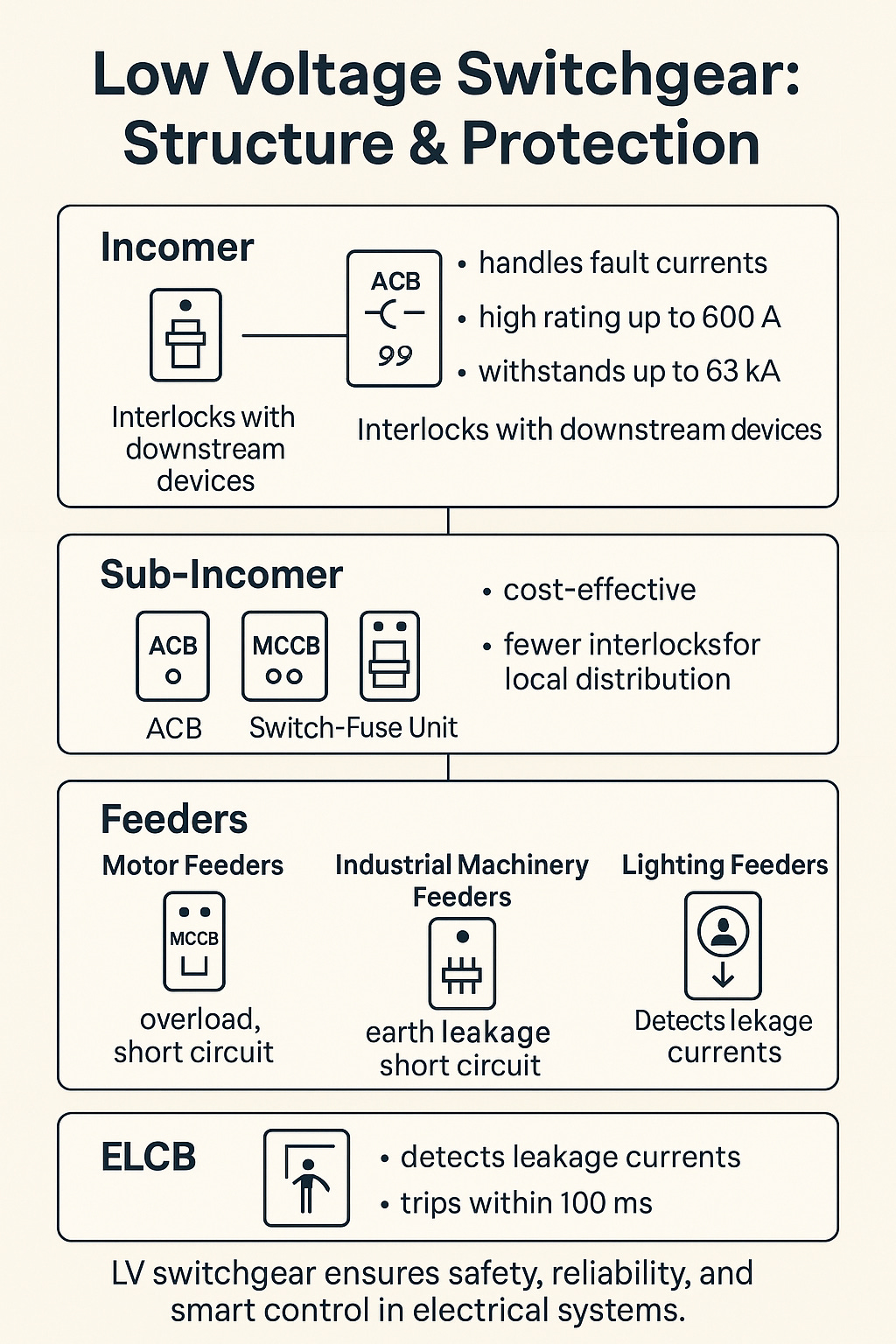
Inside an LV Distribution Board
1. Incomer Section
This is where power first enters the LV board. It feeds the incomer bus. Incomer Device Must Handle:
Short-term abnormal current (to allow downstream devices time to trip)
Full fault interruption capacity
Mechanical + electrical interlocks with downstream breakers
Preferred Device: Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs)
Why ACBs?
Simple construction
Reliable operation
High normal current rating (up to 600 A)
High fault withstand (up to 63 kA)
Despite large size & cost, they offer top-tier protection
2. Sub-Incomer Section
This part draws power from the incomer and feeds it to the feeder bus. Devices here:
ACBs
Switch-fuse units
MCCBs
Design Objectives:
Achieve cost-effectiveness without compromising protection
Fewer interlocks due to smaller coverage area
3. Feeder Section
This is where the actual load gets connected— like motors, lighting systems, air conditioning, ovens, or transformer cooling fans. Each feeder is tailored based on the load type, using a mix of:
MCCBs
Switch-fuse disconnectors
ELCBs (where leakage protection is critical)
Types of Feeders & Their Protection
1) Motor Feeders
Need to be protected from:
Overload
Short circuit
Locked rotor
Single phasing
Protection: MCCB + Thermal overload relay or motor protection circuit breaker (MPCB)
2) Industrial Machinery Load Feeders
E.g., Electroplating tanks, furnaces
Protection: MCCBs + switch-fuse units
3) Lighting Load Feeders
Here, safety is critical— due to proximity to people and structures.
Protection:
MCCBs or MCBs
Plus: Earth Leakage Protection
Why ELCBs Matter
Circuit breakers and fuses protect equipment. But what about humans? That’s where ELCBs (Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers) come in.
They trip if they detect:
Leakage current as low as 100 mA
Disconnect in <100 milliseconds
This protects against electric shocks, fires, and dangerous insulation failures.
Conclusion: LV Switchgear is More Than Just Breakers
It’s an intelligently coordinated system that:
Protects equipment
Prevents life-threatening shocks
Ensures system reliability
In a well-designed LV distribution board, every breaker and switch plays a role— from handling mega faults to reacting in milliseconds to a hairline leakage.